Food sensitivities can cause many symptoms such as Migraines, Irritable Bowel Disease, and Arthritis.
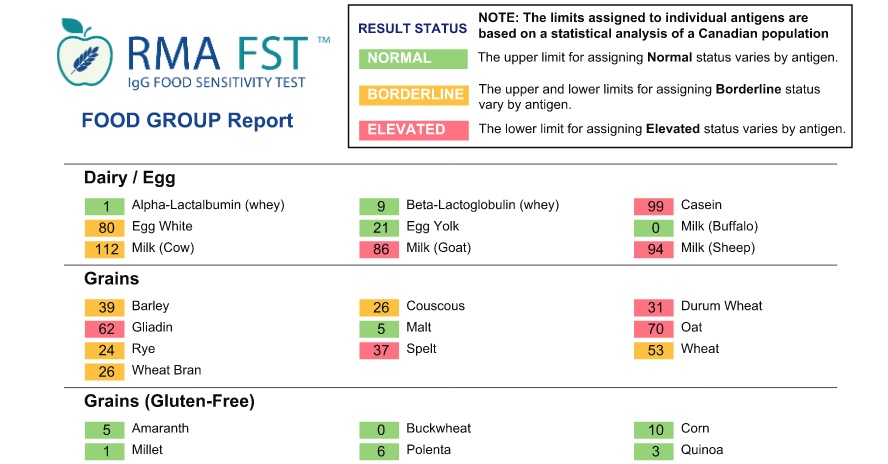
Food Sensitivity tests looks at 96-200 different foods. It is a blood test that measures the serum concentration of antibodies to specific food allergens. IgG antibodies are the potential indicator of delayed food allergies or food sensitivities. The delayed IgG antibody response often appears 1 to 3 days after exposure to the trigger food. Tiny amounts do not set off symptoms, only excess amounts—overloads. Symptoms are generalized and the delayed onset makes the cause and effect diagnosis difficult.
The symptoms range from a headache, muscle ache, tension and fatigue, to exacerbation of allergic rhinitis and asthma. The benefit of this test is that it can identify unsuspected food sensitivities, which if ignored, may result in stress on the immune system, contributing to the development of additional illness.
Usually foods that are eaten frequently would be the foods suspected in causing symptoms. High IgG levels would indicate a frequent exposure to a particular food. Individuals with inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders and dermatitis frequently have high levels of food-specific IgG antibodies. IgG food sensitivity testing is also valuable as a preventive tool for people who are not overtly experiencing symptoms.
Most extended health care plans will reimburse the patient for some or all of the cost of this test, so check with your provider. See our “Services and Fees” page for the new fees.


